How is Stock Price Decided?
Fundamental Analysis and Stock Price
How is stock price decided – Fundamental analysis assesses a company’s intrinsic value to determine whether its stock is overvalued or undervalued. This involves examining financial statements, economic conditions, and industry trends. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Company Earnings and Stock Price
A company’s earnings per share (EPS) significantly influence its stock price. Positive earnings surprises, where a company exceeds projected earnings, generally lead to price increases, reflecting investor confidence in the company’s profitability. Conversely, negative surprises often result in price drops.
Revenue Growth and Investor Sentiment
Consistent revenue growth signals a healthy and expanding business, attracting investors and pushing stock prices upward. High revenue growth, particularly when coupled with increasing profit margins, is a strong indicator of future success and value appreciation.
Debt Levels and Company Valuation
High levels of debt can negatively impact a company’s valuation and stock price. Excessive debt increases financial risk, potentially reducing investor confidence and lowering the company’s credit rating. Conversely, companies with low debt levels are often perceived as more stable and less risky.
Valuation Metrics and Stock Price Influence

Source: claytrader.com
Several valuation metrics help investors assess a stock’s worth relative to its price. The Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E) compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share. A high P/E ratio might suggest overvaluation, while a low P/E ratio could indicate undervaluation. The PEG ratio adjusts the P/E ratio for growth, providing a more nuanced view. Other metrics, such as Price-to-Sales (P/S) and Price-to-Book (P/B) ratios, offer additional perspectives on valuation.
Impact of Earnings Surprises on Stock Price
| Scenario | Impact on Stock Price | Example | Investor Sentiment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive Earnings Surprise | Increase | Company exceeds projected earnings by 10% | Positive; increased confidence in future growth |
| Negative Earnings Surprise | Decrease | Company misses projected earnings by 5% | Negative; concerns about company’s financial health |
| No Surprise | Minimal Change | Company meets projected earnings exactly | Neutral; no significant shift in investor expectations |
| Significant Positive Surprise | Sharp Increase | Unexpected breakthrough product launch leads to massive earnings increase | Extremely Positive; significant increase in future growth potential |
Technical Analysis and Stock Price: How Is Stock Price Decided
Technical analysis uses historical market data, such as price and volume, to identify patterns and predict future price movements. Unlike fundamental analysis, it doesn’t consider a company’s financial health. Instead, it focuses on chart patterns, indicators, and other market signals.
Chart Patterns and Price Predictions
Technical analysts study chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, triangles, and double tops/bottoms, to anticipate potential price reversals or breakouts. These patterns represent recurring price formations that can offer clues about future price direction.
Moving Averages and Trading Decisions
Moving averages smooth out price fluctuations, helping identify trends. Commonly used moving averages include simple moving averages (SMA) and exponential moving averages (EMA). Traders often use crossovers of different moving averages as buy or sell signals.
Key Technical Indicators and Stock Price
Technical indicators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), and Bollinger Bands, provide additional insights into price momentum, trend strength, and potential overbought or oversold conditions. These indicators are used in conjunction with chart patterns and moving averages to generate trading signals.
Comparison of Technical Analysis Methodologies
Various technical analysis methodologies exist, each with its own set of indicators and interpretations. Some focus on price action, while others emphasize volume or momentum. The choice of methodology often depends on the trader’s individual style and risk tolerance.
Hypothetical Trading Strategy Based on Technical Indicators
A hypothetical strategy might involve buying when the RSI falls below 30 (oversold condition) and the MACD crosses above its signal line, indicating a potential bullish reversal. The stop-loss order would be placed below a recent swing low. Expected outcomes depend on market conditions and accuracy of indicator signals. Risk factors include false signals and market volatility.
Market Sentiment and Stock Price
Market sentiment, encompassing investor psychology and overall market mood, significantly influences stock prices. News events, investor behavior, and social media all play a role in shaping this sentiment.
Influence of News Events on Stock Prices
Major news events, such as economic data releases (e.g., inflation reports, employment figures), geopolitical developments, and company-specific announcements (e.g., earnings reports, product launches), can cause substantial short-term price fluctuations. Positive news generally leads to price increases, while negative news often results in price declines.
Investor Psychology and Short-Term Price Fluctuations
Investor psychology, driven by emotions like fear and greed, contributes to short-term price volatility. Fear can lead to panic selling, driving prices down, while greed can fuel speculative bubbles, pushing prices artificially high.
Social Media Sentiment and Stock Price Impact
Social media platforms have become influential in shaping market sentiment. Positive or negative commentary on a particular stock can sway investor opinions and trigger price movements, sometimes leading to significant short-term volatility (e.g., the GameStop saga).
Market Trends and Individual Stock Prices
Market trends, such as bull markets (characterized by rising prices) and bear markets (characterized by falling prices), significantly affect individual stock prices. During bull markets, most stocks tend to rise, while in bear markets, most stocks decline. However, individual stock performance can deviate from the overall market trend.
Timeline Illustrating News Event Impact on Stock Price
Example: A hypothetical company, “TechCorp,” announces a groundbreaking new technology. The stock price might experience a sharp increase immediately following the announcement, followed by a period of consolidation as investors assess the long-term implications. Over time, if the technology proves successful, the stock price may continue to rise, reflecting the company’s improved prospects.
Supply and Demand and Stock Price
The fundamental principle of supply and demand governs stock prices. The interaction between buyers and sellers determines the equilibrium price, reflecting the balance between the demand for a stock and the available supply.
Changes in Share Availability and Price
Source: cheggcdn.com
A stock’s price is fundamentally determined by the interplay of supply and demand. Factors like company performance, market sentiment, and overall economic conditions all play a role. To illustrate, consider the fluctuations you might see when examining the helium one stock price ; its price reflects investor confidence in the company’s prospects and the broader market’s view of the helium market.
Ultimately, the price reflects a collective assessment of future value and risk.
Changes in the number of shares available for trading affect price. A decrease in supply (e.g., through share buybacks) can lead to price increases, while an increase in supply (e.g., through new stock issuances) can put downward pressure on prices.
Impact of Large Buy or Sell Orders on Price Volatility
Large buy orders (buying pressure) can quickly push prices up, while large sell orders (selling pressure) can cause prices to drop. This is particularly true in less liquid stocks, where large trades can significantly affect the available supply and demand balance.
Institutional vs. Retail Investors’ Impact on Supply and Demand, How is stock price decided
Institutional investors (e.g., mutual funds, hedge funds) often have a larger impact on supply and demand than retail investors due to their significantly larger trading volumes. Their investment decisions can drive significant price movements.
Visual Representation of Supply, Demand, and Stock Price
Imagine a graph with price on the vertical axis and quantity (number of shares) on the horizontal axis. The demand curve slopes downward (higher price, lower quantity demanded), while the supply curve slopes upward (higher price, higher quantity supplied). The intersection of these curves represents the equilibrium price, where the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. A shift in either the supply or demand curve (e.g., increased demand shifting the demand curve to the right) will lead to a new equilibrium price.
Regulatory Factors and Stock Price
Government regulations and policies significantly influence stock prices. Interest rate changes, accounting standards, and corporate governance rules all play a crucial role in shaping market dynamics.
Role of Government Regulations in Influencing Stock Prices
Government regulations aim to maintain market stability and protect investors. These regulations can impact stock prices through various mechanisms, including restrictions on insider trading, disclosure requirements, and rules governing mergers and acquisitions.
Impact of Interest Rate Changes on Stock Valuations
Interest rate changes affect stock valuations primarily through their impact on corporate borrowing costs and investor returns. Higher interest rates generally increase borrowing costs, potentially reducing corporate profits and making stocks less attractive. Conversely, lower interest rates can stimulate investment and boost stock valuations.
Potential Regulatory Changes Impacting Sector Stock Prices
Source: cheggcdn.com
Changes in environmental regulations could significantly affect the stock prices of companies in energy or manufacturing sectors. Similarly, stricter data privacy regulations could impact technology companies.
Accounting Scandals and Corporate Governance Issues
Accounting scandals and corporate governance failures can severely damage investor confidence and lead to sharp declines in stock prices. Examples include Enron and WorldCom, which resulted in significant losses for investors.
Key Regulatory Bodies and Their Influence on the Stock Market
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): Oversees U.S. stock markets and enforces securities laws.
- Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA): Regulates brokerage firms and exchange markets.
- Federal Reserve (The Fed): Influences monetary policy and interest rates, impacting market conditions.
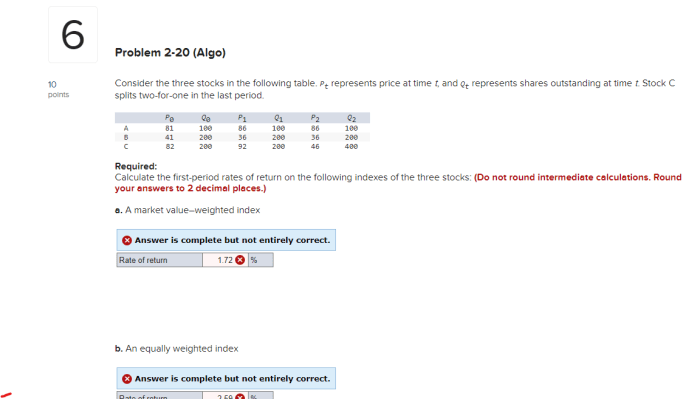
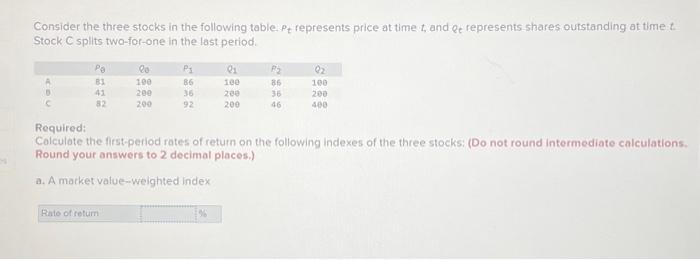
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a bull and bear market?
A bull market is characterized by rising prices and optimism, while a bear market is marked by falling prices and pessimism.
How do dividends affect stock price?
Dividends can influence stock price, often leading to a slight dip immediately after payment, but the long-term effect depends on investor perception of the dividend’s sustainability and the company’s overall prospects.
What role do short sellers play in stock price?
Short sellers borrow and sell shares, hoping to buy them back later at a lower price, profiting from the price decline. Their actions can exacerbate downward pressure on a stock’s price.
How do options contracts influence stock price?
Options contracts, giving the holder the right but not the obligation to buy or sell shares at a specific price, can influence stock price through increased trading volume and potential hedging activities.