In today’s increasingly digital world, data security is paramount. Protecting sensitive information stored on your hard drive is crucial, and hard disc encryption software provides a robust solution. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of hard drive encryption, exploring various software options, their features, and considerations for choosing the right solution for your needs. We’ll cover topics ranging from full disk encryption (FDE) to file-level encryption, addressing common concerns and providing practical advice.
Understanding Hard Drive Encryption
Hard drive encryption is the process of scrambling the data stored on your hard drive, rendering it unreadable without the correct decryption key. This acts as a powerful safeguard against unauthorized access, protecting your personal files, financial information, and other sensitive data from theft, loss, or malicious attacks. Different methods exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Let’s examine the key types:
Full Disk Encryption (FDE), Hard disc encryption software
Full disk encryption, as the name suggests, encrypts the entire hard drive, including the operating system, applications, and user data. This provides the highest level of security, protecting everything on the drive. Popular FDE solutions often integrate directly with the operating system, making the encryption process transparent to the user. Examples include BitLocker (Windows), FileVault (macOS), and LUKS (Linux).
The key advantage is comprehensive protection; however, it can impact performance slightly.
File-Level Encryption
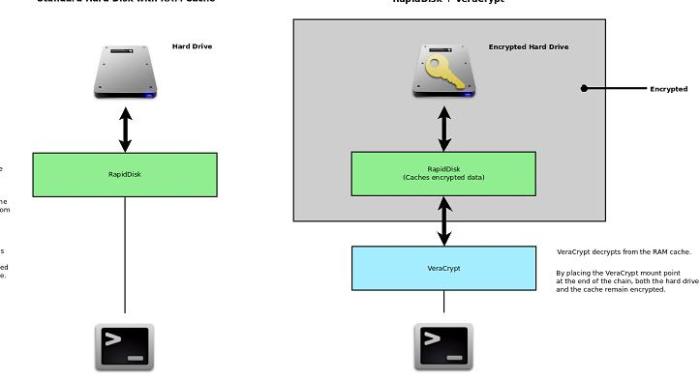
File-level encryption, in contrast, encrypts individual files or folders. This offers a more granular approach to security, allowing users to selectively encrypt sensitive data while leaving less critical information unencrypted. This method is generally less resource-intensive than FDE, but requires more active management from the user. Examples include VeraCrypt and 7-Zip with encryption capabilities. The choice between FDE and file-level encryption depends on individual needs and security priorities.
Source: open-pr.com
Hardware vs. Software Encryption
While software encryption utilizes software to perform the encryption and decryption processes, hardware encryption leverages specialized hardware components, such as a Trusted Platform Module (TPM), to enhance security. Hardware encryption often offers faster speeds and enhanced protection against certain attacks. Many modern systems incorporate TPMs, allowing for a hybrid approach combining both hardware and software encryption for optimal security.
Choosing the Right Hard Disc Encryption Software
Selecting the appropriate hard drive encryption software depends on several factors:
- Operating System Compatibility: Ensure the software is compatible with your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Encryption Algorithm: Strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, are crucial for robust security. Research the algorithms used by different software options.
- Ease of Use: Consider the user interface and overall ease of use. Some software offers more intuitive interfaces than others.
- Performance Impact: While encryption adds a layer of security, it can impact system performance. Evaluate the potential performance overhead before making a decision.
- Cost: Software options range from free and open-source to commercial solutions with varying pricing structures.
- Key Management: Understand how the software manages encryption keys. Robust key management practices are essential for data security.
Popular Hard Disc Encryption Software Options
Several reputable software options are available for hard drive encryption. Here are a few examples:
- BitLocker (Windows): Built-in full disk encryption for Windows operating systems.
- FileVault (macOS): Apple’s built-in full disk encryption for macOS.
- VeraCrypt: A free, open-source, and cross-platform disk encryption software offering both full disk and file-level encryption.
- LUKS (Linux Unified Key Setup): A standard for disk encryption on Linux systems.
- 7-Zip (with encryption): A popular file archiver that supports encryption for individual files and folders.
Security Best Practices for Hard Disc Encryption
Even with robust encryption software, maintaining good security practices is vital:
- Strong Passwords: Use long, complex, and unique passwords for your encryption keys.
- Regular Updates: Keep your encryption software updated to benefit from the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Backup Your Keys: Securely back up your encryption keys in case you lose access to them.
- Secure Storage: Store your backup keys in a safe and secure location, preferably offline.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): If available, enable 2FA for an added layer of security.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: Is hard drive encryption necessary? A: The necessity of hard drive encryption depends on the sensitivity of your data. If you store sensitive personal information, financial data, or confidential business documents, encryption is highly recommended.
- Q: Will hard drive encryption slow down my computer? A: Encryption can slightly impact performance, but modern encryption algorithms and hardware acceleration minimize this effect.
- Q: What happens if I forget my encryption key? A: If you forget your encryption key, you will lose access to your encrypted data. This underscores the importance of securely backing up your keys.
- Q: Can I encrypt a USB drive? A: Yes, many encryption software options allow you to encrypt external drives, including USB drives.
- Q: Is hardware encryption better than software encryption? A: Hardware encryption often offers faster speeds and enhanced security against certain attacks, but software encryption remains a viable option for many users.
Conclusion: Hard Disc Encryption Software
Hard disc encryption software is a crucial tool for protecting your valuable data. By understanding the different types of encryption, choosing the right software, and following best practices, you can significantly enhance your data security. Don’t wait until it’s too late – protect your information today!
References
Call to Action
Ready to safeguard your valuable data? Explore the encryption software options discussed in this guide and choose the best solution for your needs. Start protecting your digital assets today!
Query Resolution
What are the different types of hard disc encryption?

Source: justpaste.it
Common types include full disk encryption (FDE), which encrypts the entire drive, and file-level encryption, which encrypts individual files or folders.
How do I recover my data if I forget my encryption key?
Data recovery is extremely difficult or impossible if the encryption key is lost. Robust key management practices, such as securely storing backup keys, are crucial.
Is hard disc encryption software compatible with all operating systems?
Compatibility varies depending on the specific software. Check the software’s system requirements before installation.
Does hard disc encryption slow down my computer?
Encryption can slightly impact performance, but modern hardware and software minimize this effect. The impact varies depending on the encryption method and hardware capabilities.
Is hard disc encryption enough to protect my data from all threats?
While highly effective, hard disc encryption is part of a broader security strategy. It’s essential to combine it with other security measures, such as strong passwords and regular software updates.
